Abstract
Introduction: In patients with Large B-cell Lymphoma (LBCL) the prognostic significance of MYC translocations is not clearly established. We aimed to investigate if additional identification of MYC translocation partner gene and/or MYC and BCL2 protein expression levels could improve patient prognostication associated with MYC translocations. We also wanted to evaluate the prognostic effect of double hit MYC + BCL2/BCL6 translocation (DH) compared to MYC single hit (SH).
Methods: A consecutively collected training cohort of 64 patients and an independent validation cohort of 28 patients all with MYC translocation positive LBCL were investigated. Translocations were identified with fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) and MYC and BCL2 protein expression with immunohistochemistry (IHC).
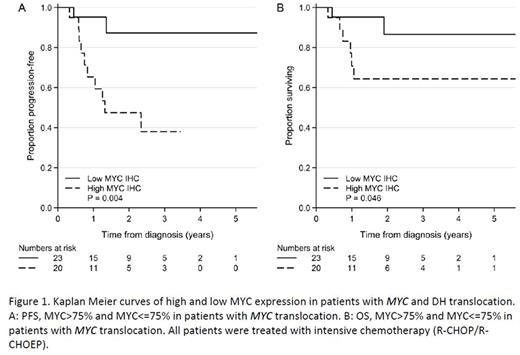
Results: MYC> 75% was seen in 50% of patients and was related to frequent bone marrow involvement, high IPI and elevated LDH. MYC>75% was also significantly associated with reduced progression free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) in univariate analysis (PFS: HR 6.8 (95%CI 1.5-31), p=0.004. OS: HR 4.3 (95%CI 0.9-21), p=0.05) (Fig. 1). In multivariable analysis adjusting for IPI MYC>75% was independently prognostic for PFS but not OS (PFS: HR 5.4 (95%CI 1.1-25), p=0.04. OS: HR 3.1 (95%CI 0.6-16), p=0.2). DH was seen in 71% of patients and did not confer a worse outcome compared to MYC SH. Immunoglobulin (IG) MYC translocation partner gene was found in 55% and was related to MYC protein expression levels (p=0.047). Translocation partner gene was not prognostic for PFS (p=0.8) or OS (p=0.6). High BCL2 expression was related to high MYC expression (p=0.003) and did not add to the prognostic effect observed for MYC. The findings were confirmed in a comparable, independent validation cohort of 28 MYC translocation positive LBCL. The patients included in the survival analyses were treated with R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine and prednisone) or R-CHOEP (R-CHOP + etoposide).
Conclusions: These findings suggest that stratification by MYC protein expression level significantly improves the prognostic impact of MYC translocation in patients with large B-cell lymphoma.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal